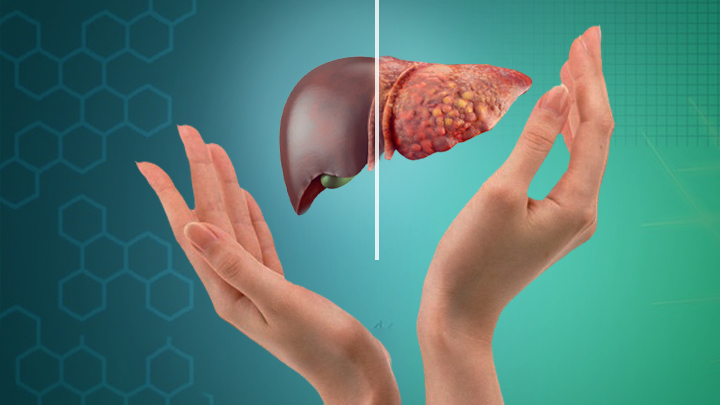
Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is commonly referred to as a lifestyle disease because it is strongly associated with certain lifestyle choices and habits. It is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells, leading to impaired liver function. While there can be other contributing factors, lifestyle choices play a significant role in the development and progression of fatty liver. Here are some key reasons why fatty liver is considered a lifestyle disease:
- Poor Diet: A diet high in saturated fats, processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive calories can contribute to the development of fatty liver. These dietary choices lead to increased fat deposition in the liver and promote inflammation, ultimately causing liver damage.
- Obesity: Excess body weight, especially abdominal obesity, is strongly associated with fatty liver. Obesity alters the way the body metabolizes and stores fat, leading to the accumulation of fat in the liver. It also increases the risk of other metabolic conditions, such as insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, which further contribute to fatty liver development.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle are major risk factors for fatty liver. Regular exercise helps in maintaining a healthy weight, improves insulin sensitivity, and promotes the breakdown of fat in the liver. On the other hand, a sedentary lifestyle promotes fat accumulation and increases the risk of liver diseases.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol abuse is a leading cause of fatty liver, known as alcoholic fatty liver disease. Regular and excessive alcohol consumption leads to fat deposition in the liver, inflammation, and liver damage. It is important to note that even moderate alcohol consumption can contribute to fatty liver in susceptible individuals.
- Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome: Insulin resistance, a condition in which cells fail to respond properly to insulin, is commonly associated with fatty liver. Insulin resistance is often seen in individuals with obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. These conditions are closely linked to poor lifestyle choices and are major risk factors for fatty liver.
- Smoking: Although smoking is primarily associated with lung diseases, it can also contribute to fatty liver. Smoking increases oxidative stress and inflammation in the liver, promoting liver damage and fat accumulation.
- Medications and Toxins: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, tamoxifen, and methotrexate, as well as exposure to toxins and pollutants, can contribute to the development of fatty liver. While these factors may not be directly related to lifestyle choices, avoiding unnecessary medication use and minimizing exposure to toxins are part of a healthy lifestyle.
It is important to understand that fatty liver is a progressive condition, and if left untreated, it can lead to more severe liver diseases such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. However, the good news is that fatty liver is largely reversible through lifestyle modifications. Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, Herbal remedies, regular physical activity, weight management, limited alcohol consumption, and avoiding smoking can significantly reduce the risk of fatty liver and its progression.
In conclusion, fatty liver is considered a lifestyle disease due to its strong association with poor dietary choices, sedentary behavior, obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, and other lifestyle factors. By making positive lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of developing fatty liver and improve liver health overall. It is always advisable to consult with a Ayurvedic Doctor or healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support in managing and Ayurvedic treatment of fatty liver.